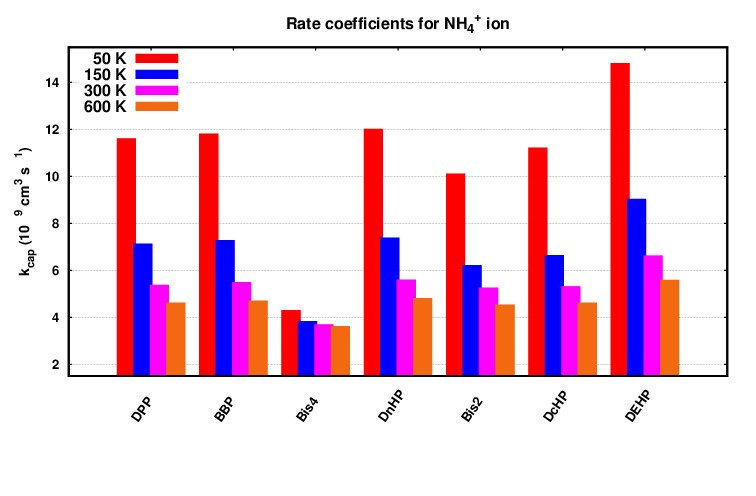
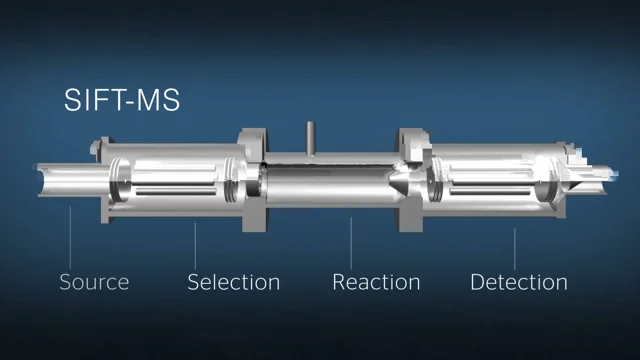
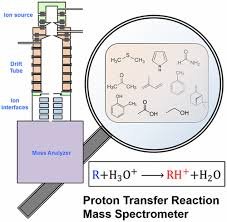
These computed molecular parameters, including dipole moment, polarizability, proton affinity, and ionization energy of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), are crucial for the identification and quantification of VOCs in chemical ionization…
Development of a Molecular Properties Database for Enhanced Chemical Ionization Mass Spectrometry in Trace Gas Analysis